Working with Git in PyCharm
This is the basic workflow when working with Git with PyCharm. For the CLI version of the guide, click here. The following will use the Sir-Lancebot repository as an example, but the steps are the same for all other repositories.
Note: This is a guide only meant to get you started with git. For in-depth resources, check the Working with Git page.
Adding the Upstream Remote¶
Adding a remote to the main GitHub repository you forked off will allow you to later update your fork with changes from the main repository.
Generally, a remote designates a repository that is on GitHub or another external location rather than on your computer. The
originremote will refer to your fork on GitHub. Theupstreamremote will refer to the main repository on GitHub.
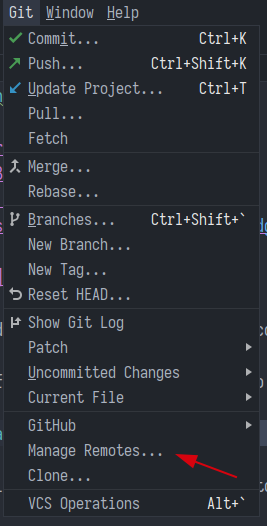
- In the menu bar, navigate to
Git->Remotes....
- In the popup menu, click the
+icon, setupstreamas the name, set the URL as the URL for the main repository on GitHub.
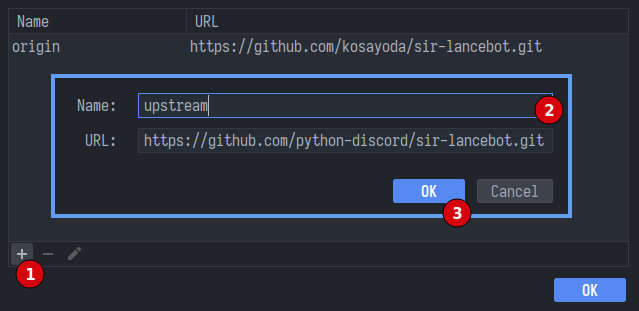
- Click
OK.
Creating a New Branch¶
You will be committing your changes to a new branch rather than to
main. Using branches allows you to work on multiple pull requests at the same time without conflicts.You can name your branch whatever you want, but it's recommended to name it something succinct and relevant to the changes you will be making.
Before making new branches, be sure to checkout the
mainbranch and ensure it's up to date.
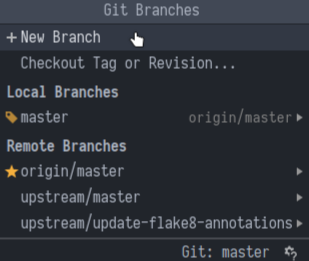
- In the bottom right corner, click on
mainand then clickNew Branch.
Committing Changes¶
After making changes to the project files, you can commit by clicking the commit button that's part of the Git actions available in the top right corner of your workspace:
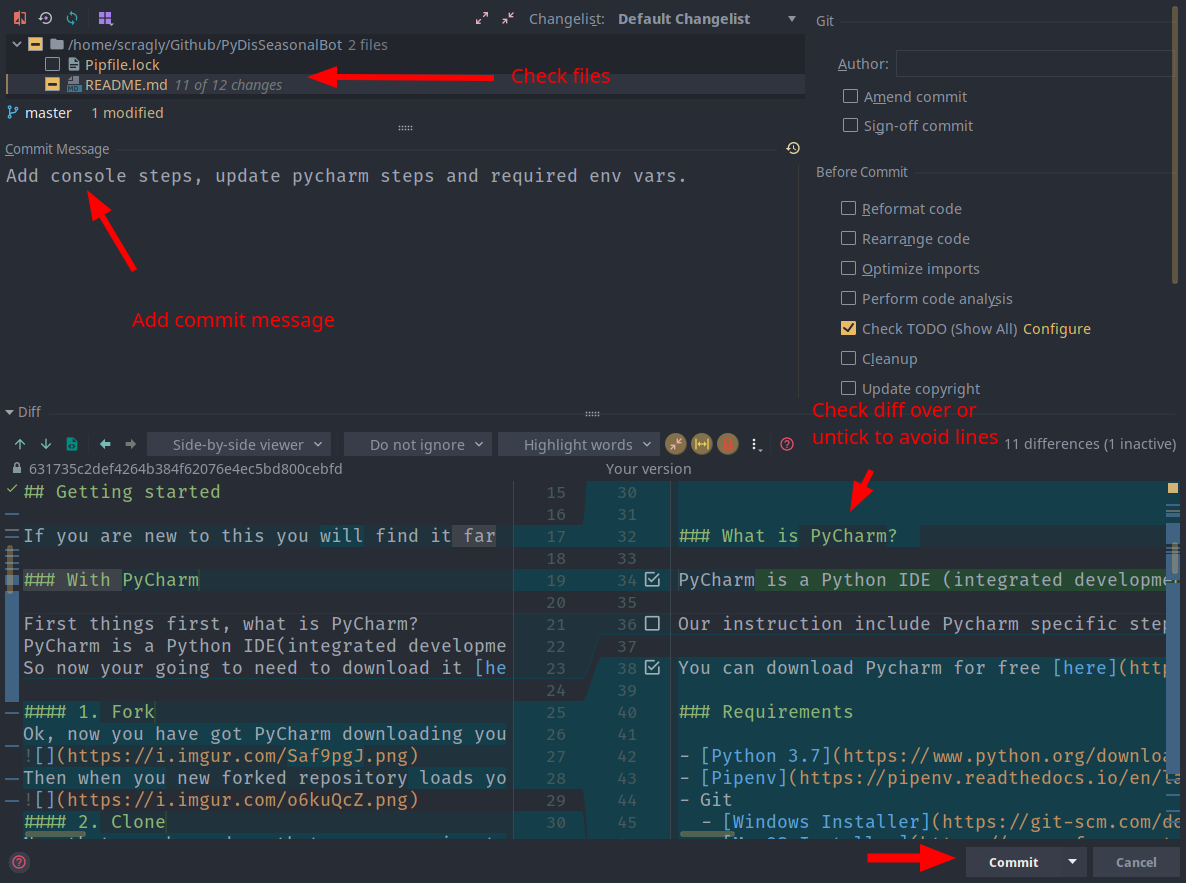
The flow of making a commit is as follows:
- Select the files you wish to commit.
- Write a brief description of what your commit is. This is your commit message.
- See the actual changes your commit will be making, and optionally tick/untick specific changes to only commit the changes you want.
- Click
Commit.
Pushing Changes¶
When you are ready to have your commits be available in your remote fork, navigate to Git -> Push....
Select the commits you want to push, make sure the remote branch is your intended branch to push to, and click Push.
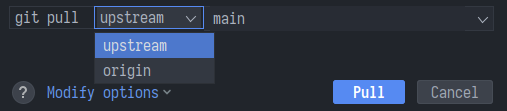
Pulling Changes¶
Sometimes you want to update your repository with changes from GitHub. This could be the case if you were working on the pull request on two different computers and one of them has an outdated local repository.
To do that, navigate to Git -> Pull.... From there, select the remote and the branches to pull from, then click Pull.